WTF Ethers: 17. MerkleTree Script
I've been revisiting ethers.js recently to refresh my understanding of the details and to write a simple tutorial called "WTF Ethers" for beginners.
Twitter: @0xAA_Science
Community: Website wtf.academy | WTF Solidity | discord | WeChat Group Application
All the code and tutorials are open-sourced on GitHub: github.com/WTFAcademy/WTF-Ethers
In this lesson, we will write a script that utilizes the Merkle Tree to whitelist addresses for minting NFTs. If you are not familiar with the Merkle Tree contract, please refer to WTF Solidity 36: Merkle Tree.
Merkle Tree
A Merkle Tree, also known as a hash tree, is a fundamental cryptographic technology used in blockchain systems, including Bitcoin and Ethereum. A Merkle Tree is a bottom-up constructed binary tree, where each leaf node represents the hash of some data, and each non-leaf node represents the hash of its two child nodes.
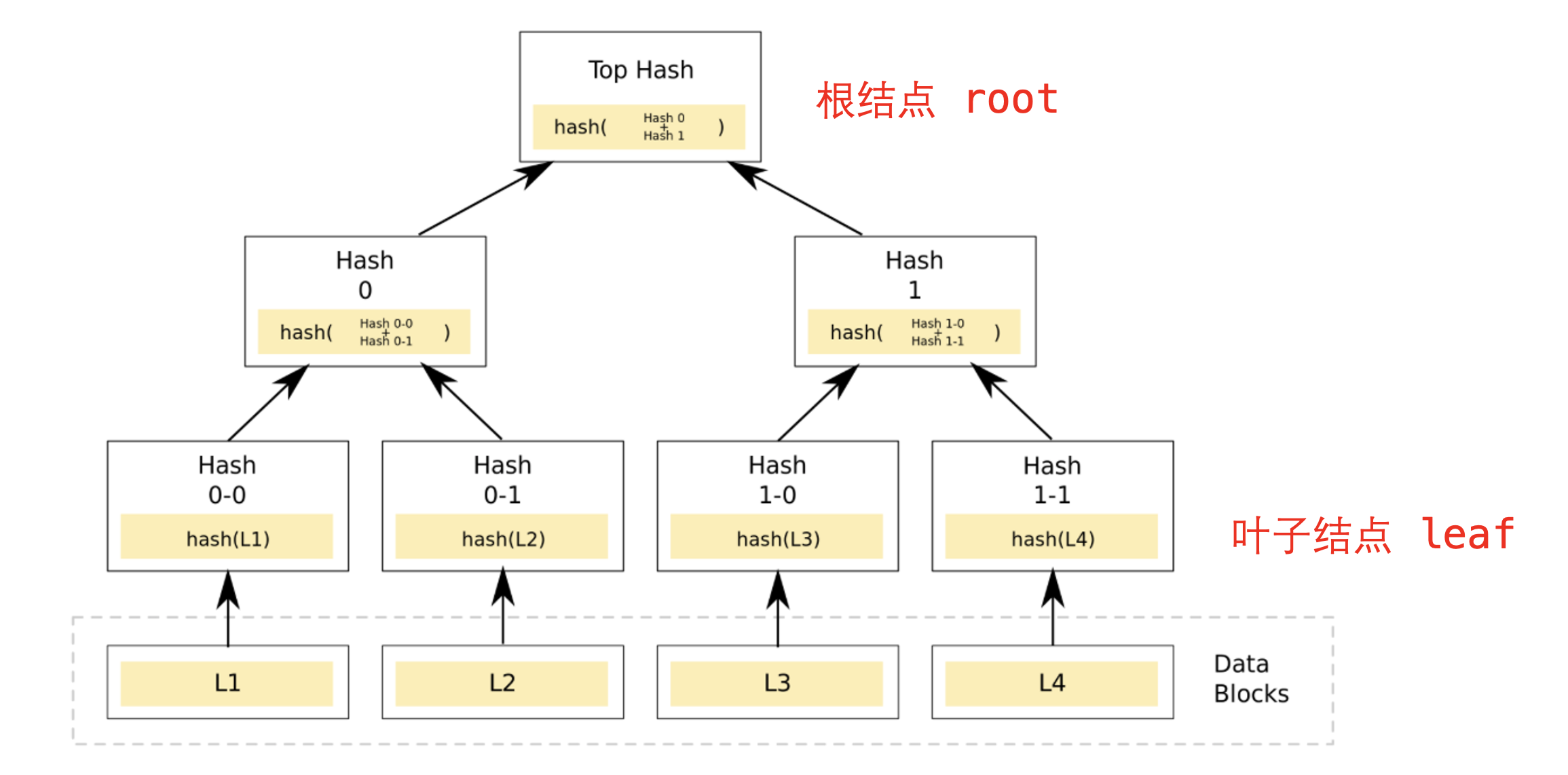
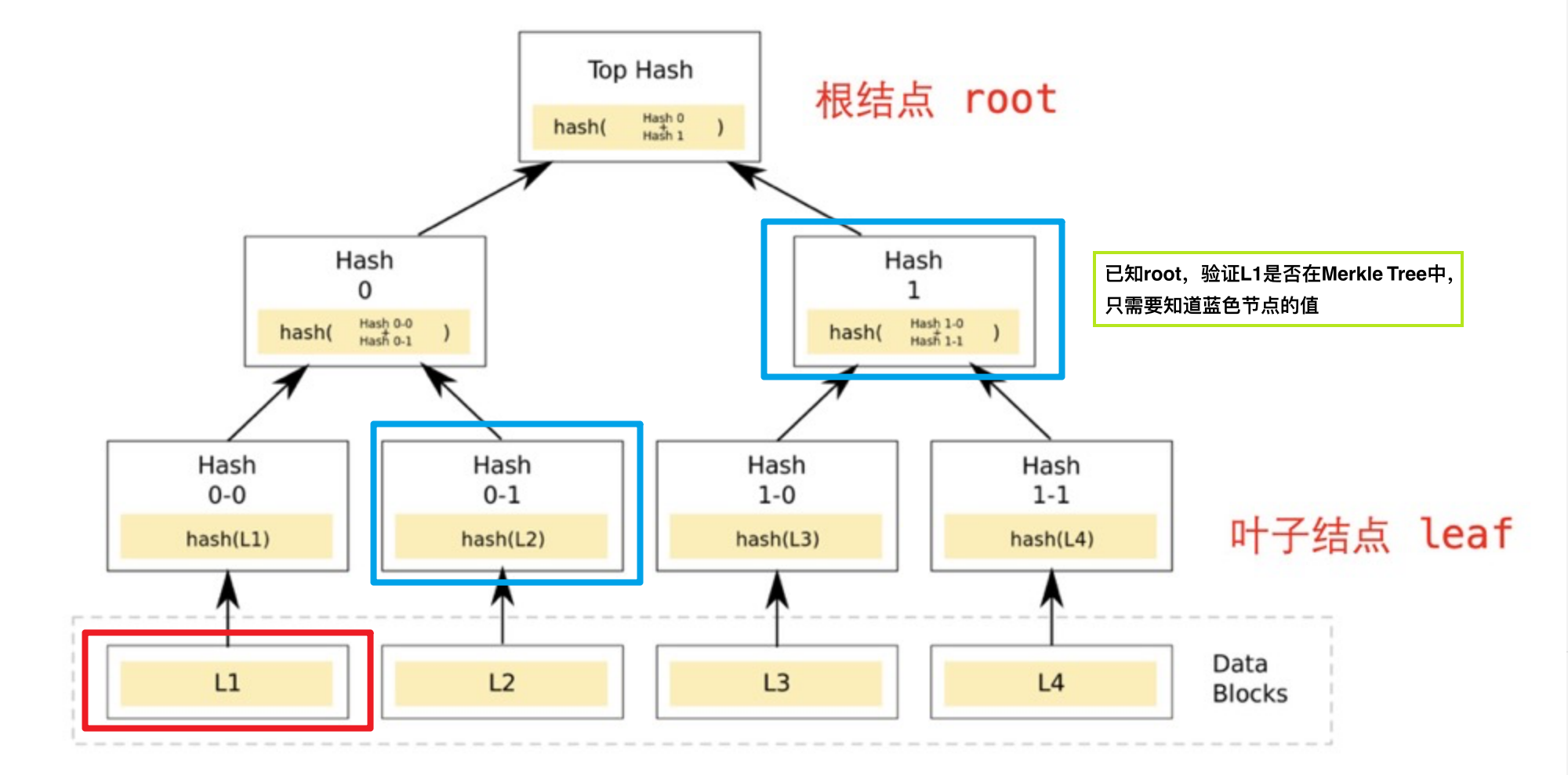
The Merkle Tree allows for efficient and secure verification of large data structures (Merkle Proof). For a Merkle Tree with N leaf nodes, given the known root value, verifying whether a specific data is valid (belonging to a leaf node of the Merkle Tree) only requires log(N) data (also known as a proof), which is highly efficient. If the data is incorrect or the provided proof is wrong, it is not possible to obtain the root value. In the example below, the Merkle proof for leaf L1 includes "Hash 0-1" and "Hash 1": knowing these two values allows us to verify if the value of L1 is present in the Merkle Tree's leaf nodes.
Merkle Tree Contract Overview
In WTF Solidity 36: Merkle Tree, the MerkleTree contract is used to validate whitelisted addresses for minting NFTs. Let's briefly explain the two functions used here:
Constructor: Initializes the name, code, and root of merkle tree of the NFT contract.
mint(): Uses the Merkle Proof to validate the whitelisted address and mint the NFT. The function parameters are the whitelisted addressaccount, thetokenIdto be minted, and theproof.
MerkleTree.js
MerkleTree.js is a JavaScript package for building Merkle Trees and generating Merkle Proofs (Github link). You can install it via npm:
npm install merkletreejs
Here, we demonstrate how to generate a Merkle Tree with leaf nodes containing 4 whitelisted addresses.
Create an array of whitelisted addresses.
import { MerkleTree } from "merkletreejs";
// Whitelisted addresses
const tokens = [
"0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4",
"0xAb8483F64d9C6d1EcF9b849Ae677dD3315835cb2",
"0x4B20993Bc481177ec7E8f571ceCaE8A9e22C02db",
"0x78731D3Ca6b7E34aC0F824c42a7cC18A495cabaB"
];Hash the data using
keccak256(matching the hashing function used in Solidity) to create the leaf nodes.const leaf = tokens.map(x => ethers.keccak256(x))Create the Merkle Tree, using
keccak256as the hashing function. The optional parametersortPairs: truekeeps the same processing logic as the Merkle Tree contract.const merkletree = new MerkleTree(leaf, ethers.keccak256, { sortPairs: true });Get the
rootof the Merkle Tree.const root = merkletree.getHexRoot()Get the
prooffor the leaf node at index0.const proof = merkletree.getHexProof(leaf[0]);
Whitelist Address Token Minting with Merkle Tree
Here, we provide an example of how to validate a whitelist and mint NFTs using MerkleTree.js and ethers.js.
Generate the Merkle Tree.
// 1. Generate Merkle Tree
console.log("\n1. Generate Merkle Tree")
// Whitelisted addresses
const tokens = [
"0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4",
"0xAb8483F64d9C6d1EcF9b849Ae677dD3315835cb2",
"0x4B20993Bc481177ec7E8f571ceCaE8A9e22C02db",
"0x78731D3Ca6b7E34aC0F824c42a7cC18A495cabaB"
];
// Leaf, Merkle Tree, Proof
const leaf = tokens.map(x => ethers.keccak256(x))
const merkletree = new MerkleTree(leaf, ethers.keccak256, { sortPairs: true });
const proof = merkletree.getHexProof(leaf[0]);
const root = merkletree.getHexRoot()
console.log("Leaf:")
console.log(leaf)
console.log("\nMerkle Tree:")
console.log(merkletree.toString())
console.log("\nProof:")
console.log(proof)
console.log("\nRoot:")
console.log(root)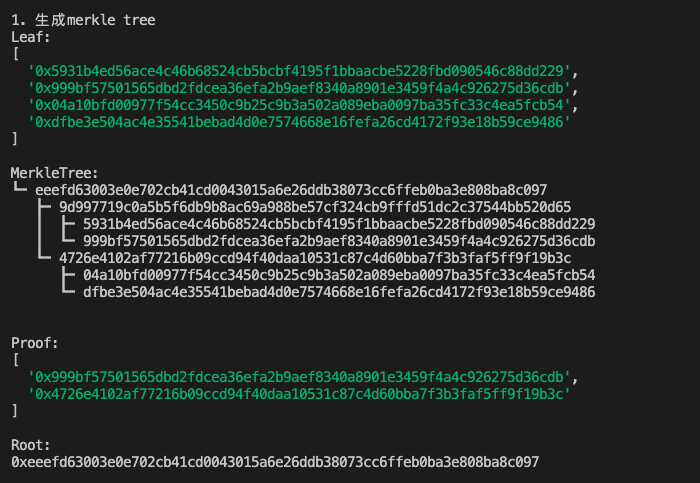
Create provider and wallet.
```js
// Prepare Alchemy API - refer to https://github.com/AmazingAng/WTF-Solidity/blob/main/Topics/Tools/TOOL04_Alchemy/readme.md
const ALCHEMY_GOERLI_URL = 'https://eth-goerli.alchemyapi.io/v2/GlaeWuylnNM3uuOo-SAwJxuwTdqHaY5l';const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider(ALCHEMY_GOERLI_URL); // Create wallet object using private key and provider const privateKey = '0x227dbb8586117d55284e26620bc76534dfbd2394be34cf4a09cb775d593b6f2b' const wallet = new ethers.Wallet(privateKey, provider)
```Create contract factory to prepare for deploying the contract.
// 3. Create contract factory
// NFT ABI
const abiNFT = [
"constructor(string memory name, string memory symbol, bytes32 merkleroot)",
"function name() view returns (string)",
"function symbol() view returns (string)",
"function mint(address account, uint256 tokenId, bytes32[] calldata proof) external",
"function ownerOf(uint256) view returns (address)",
"function balanceOf(address) view returns (uint256)",
];
// Contract bytecode, in remix, you can find the Bytecode in two places
// i. Bytecode button in the deploy panel
// ii. In the json file with the same name as the contract in the artifact folder in the file panel
// The data corresponding to the "object" field is the Bytecode, quite long, starting with 608060
// "object": "608060405260646000553480156100...
const bytecodeNFT = contractJson.default.object;
const factoryNFT = new ethers.ContractFactory(abiNFT, bytecodeNFT, wallet);Deploy the NFT contract using the contract factory
console.log("\n2. Deploy the NFT contract using the contract factory")
// Deploy the contract and fill in the constructor parameters
const contractNFT = await factoryNFT.deploy("WTF Merkle Tree", "WTF", root)
console.log(`Contract address: ${contractNFT.target}`);
console.log("Waiting for the contract to be deployed on chain")
await contractNFT.waitForDeployment()
console.log("Contract deployed")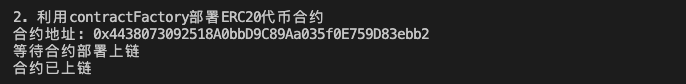
Call the
mint()function to validate the whitelist using the merkle tree and mint an NFT for the first address. After successful minting, the NFT balance will be 1.console.log("\n3. Call the mint() function to validate the whitelist using the merkle tree and mint an NFT for the first address")
console.log(`NFT name: ${await contractNFT.name()}`)
console.log(`NFT symbol: ${await contractNFT.symbol()}`)
let tx = await contractNFT.mint(tokens[0], "0", proof)
console.log("Minting, waiting for the transaction to be confirmed on chain")
await tx.wait()
console.log(`Mint successful, NFT balance for address ${tokens[0]}: ${await contractNFT.balanceOf(tokens[0])}\n`)
For Production
To use the Merkle Tree to validate whitelist and issue NFTs in production, follow these steps:
- Determine the whitelist.
- Generate the Merkle Tree for the whitelist on the backend.
- Deploy the NFT contract and save the root of the Merkle Tree in the contract.
- When a user wants to mint, request the
proofcorresponding to the address from the backend. - The user can then call the
mint()function to mint the NFT.
Summary
In this lesson, we introduced the Merkle Tree and used MerkleTree.js and ethers.js to create, validate whitelist, and mint NFTs.